


Page 4/10 |
Defining the 4Es: Education, Esthetics, Escapism, and Entertainment
The Experience Economy offers four realms of experiential value to add to a business. Pine and Gilmore (1999) termed these realms, the 4Es. The 4Es consist of adding Educational, Esthetic,
Escapist, and Entertainment experiences to the business. The four experiences vary based on the customer’s active or passive participation and on absorption or immersion in the experience. Active – passive participation entails the level of customer involvement in creation of the experience.
For instance, the customer can actively participate in a product trial or passively watch a product demonstration performed by a staff member. Absorption is “occupying customers’ attention by bringing the experience into the mind” and immersion is “becoming physically or virtually a part of the experience itself” (Pine & Gilmore, 1999, p. 31).
The 4Es are differentiated by the form of customer involvement as shown in Figure 1.3. Passive participation of the customer in an experience offered by the business characterizes the Entertainment and Esthetic dimensions, while active participation characterizes Educational and Escapist experiences. The customer who passively participates in an experiential activity or setting does not directly affect or influence these experiential offerings, whereas an active participant will personally affect these activities and settings. The customer typically “absorbs” Entertainment and Educational experiences and “immerses” in Esthetic and Escapist experiences.
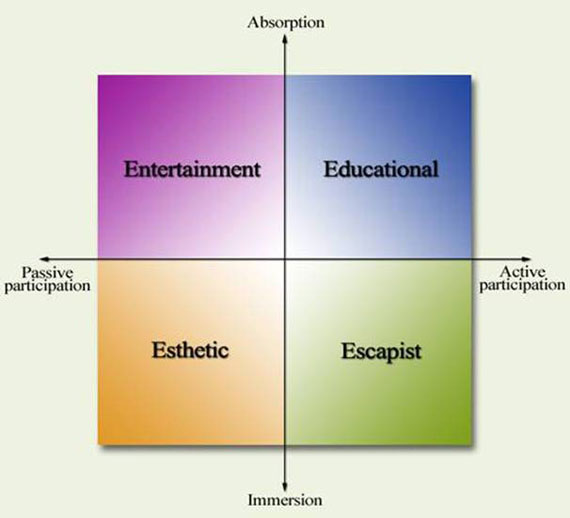
Figure 1.3
Page 4/10 |
Web site and all contents © Copyright SRDC 2009, All rights reserved. |
|
| These materials were developed as part of the Southern Rural Development Center’s National e-Commerce Extension Initiative. They are based upon work supported by the Cooperative State Research, Education, and Extension Service, U.S. Department of Agriculture, under Award No. 2005-45064-03212 Any opinions, findings, conclusions, or recommendations expressed in this publication are those of the author(s) and do not necessarily reflect the view of the U.S. Department of Agriculture or the Southern Rural Development Center. |
|